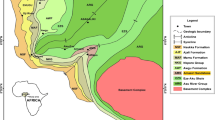
The glaciation-induced base-level fall and basin physiography straightforward controls fluvial style in any coastal setting. An alternate climatic influence including warm and cold (glacial) conditions may result in marine onlap with interception by unconformity formation and fluvial incursion in a coastal stratigraphic record. Unconformably overlying the marine sediments, the fluvial sandstone in the upper part of Pliocene Sandhan Formation is studied herein for documentation of architectural element and variability in the fluvial sedimentation motif, if any, in space-time framework. The identified architectural elements include channel (CH), gravel bar and bedforms (GB), sandy bedforms (SB), downstream accretion (DA), sediment gravity flow (SG), compound bar (CB) overbank fines (OF) and paleosol (P). From dominance of coarse-grained, granular pebbly sandstone with SB, GB, SG and DA elements, and incidence of 6–12 m thick fining-upward cycles, it is inferred that the Sandhan fluvial system was of Donjek-type braided in character. Only at the Nagmati River section in the south-east, a change in fluvial character is recorded as Platte-type. A role of basin physiography involving median-high across the depositional profile is identified from (i) decrease in thickness of fluvial deposit from north-west to south-southeast, and (ii) reduction in topographic-gradient in the south-southeast. Considering the Pliocene time frame, the fluvial incursion onto the marine system within Sandhan depositional history is identified as a result of base-level fall under influence of global glaciation.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams M M and Bhattacharya J P 2005 No change in fluvial style across a sequence boundary, Cretaceous Blackhawk and Castlegate formations of central Utah, USA; J. Sedim. Res. 75 1038–1051.
Allen J R L 1974 Studies in fluviatile sedimentation: Implications of pedogenic carbonate units, lower old red sandstone, Anglo-Welsh outcrop; Geol. J. 9 181–208.
Allen J R L 1983 Studies in fluviatile sedimentation: Bars, bar-complexes and sandstone sheets (low-sinuosity braided streams) in the brownstones (L. Devonian), Welsh Borders; Sedim. Geol. 33 237–293.
Ashley G M 1990 Classification of large-scale subaqueous bedforms: A new look at an old problem; J. Sedim. Petrol. 60 160–172.
Bajpai S, Thewissen J G M, Kapur V V, Tiwari B N and Sahni A 2006 Eocene and oligocene sirenians (Mammalia) from Kachchh, India; J. Vert. Paleont. 26(2) 400–410.
Banerjee S, Chattoraj S L, Saraswati P K, Dasgupta S, Sarkar U and Bumby A 2012a The origin and maturation of lagoonal glauconites: A case study from the Oligocene Maniyara Fort formation, western Kutch, India; Geol. J. 47 357–371.
Banerjee S, Chattoraj S L, Saraswati P K, Dasgupta S and Sarkar U 2012b Substrate control on formation and maturation of glauconites in the Middle Eocene Harudi Formation, western Kutch, India; Mar. Pet. Geol. 30 144–160.
Banerjee S, Khanolkar S and Saraswati P K 2018 Facies and depositional settings of the middle Eocene-Oligocene carbonates in Kutch; Geodinamica Acta 30(1) 119–136.
Biswas S K 1965 A new classification of the tertiary rocks of Kutch, Western India; Quat. J. Geol. Mineral. Metallur. Soc. India Bull. 35 1–6.
Biswas S K 1971 Note on the geology of Kutch; Quat. J. Geol. Mineral. Metallur. Soc. India 43(4) 223–235.
Biswas S K 1973 Time stratigraphic classification of the tertiary rocks of Kutch—A revision and amendments; Quat. J. Geol. Mineral. Metallur. Soc. India 44(3) 29–37.
Biswas S K 1982 Rift basins in western margin of India and their hydrocarbon prospects with special reference to Kutch basin; AAPG Bull. 66(10) 1497–1513.
Biswas S K 1987 Regional tectonic framework, structure and evolution of the western marginal basins of India; Tectonophys. 135(4) 307–327.
Biswas S K 1992 Tertiary stratigraphy of Kutch; J. Palaeontol. Soc. India 37 1–29.
Biswas S K and Deshpande S V 1970 Geological and tectonic maps of Kutch; Bull. Oil Nat. Gas Comm. 7(2) 115–116.
Biswas S K and Khatri K N 2002 A Geological study of earthquakes in Kutch, Gujarat, India; J. Geol. Soc. India 60 131–142.
Blodgett R H and Stanley K O 1980 Stratification, bedforms and discharge relations of the platte river system, Nebraska; J. Sedim. Petrol. 50 139–148.
Blum M D and Tornqvist T E 2000 Fluvial response to climate and sea level change: A review and look forward; Sedimentology 47(1) 2–48.
Bose P K, Sarkar S, Mukhopadhyay S, Saha B and Eriksson P 2008 Precambrian basin-margin fan deposits: Mesoproterozoic Bagalkot Group, India; Precamb. Res. 162(1–2) 264–283.
Bridge J S 2006 Fluvial facies models: Recent developments; In: Facies models revisited (eds) Posamentier, Henry W and Walker R G, SEPM (Soc. Sedim. Geol.) Spec. Publ. 84 85–170.
Bristow C S and Best J L 1993 Braided rivers: Perspectives and problems; Geol. Soc. London, Spec. Publ. 75(1) 1–11.
Burkham D E 1972 Channel changes of the Gila river in Safford Valley, Arizona, US; Geol. Surv. 24 655.
Cant D J and Walker R G 1978 Fluvial processes and facies sequences in the sandy braided south saskatchewan river, Canada; Sedimentology 25 625–648.
Castradori D, Rio D, Hilgen F J and Lourens L J 1998 The Global standard stratotype-section and point (GSSP) of the piacenzian stage (Middle Pliocene); Episodes 21 88–93.
Catuneanu O 2006 Principles of sequence stratigraphy; 1st edn, Elsevier, Oxford, 374p.
Catuneanu O and Dave A 2017 Cenozoic sequence stratigraphy of the Kachchh Basin, India; Mar. Pet. Geol. 86 1106–1132.
Chattoraj S L, Banerjee S, Saraswati P K and Bansal U 2016 Origin, depositional setting and stratigraphic implications of palaeogene glauconite of Kutch; Geol. Soc. India, Spec. Publ. 6 75–88.
Church M and Rood K 1983 Catalogue of alluvial river channel regime data; University of British Columbia, Department of Geography Vancouver, BC, 99p.
Collinson J D 1970 Bedforms of the Tana river, Norway; Geogr. Ann. 52A 31–55.
Crowley R D 1983 Large scale bed configurations (Macroform), Platt river basin Colorado and Nebraska–Primary structure and formative processes; Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 94 117–133.
Dekens P S, Ravelo A C, McCarthy M D and Edwards C A 2008 A 5 million year comparison of Mg/Ca and alkenone paleothermometers; Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 9(10).
Finzel E S and McCarthy P J 2005 Architectural analysis of fluvial conglomerate in the Nanushuk Formation, Brooks Range foothills, Alaska; Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys Preliminary Investigative Report (2) 19.
Fluger P and Seilacher A 1991 Flash flood conglomerates; In: Cycles and events in stratigraphy (eds) Einsele G, Ricken W and Seilacher A, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, New York, pp. 383–391.
Friend P F 1983 Towards the field classification of alluvial architecture or sequence; In: Modern and ancient fluvial systems (eds) Collinson J D and Lewin J, Int. Assoc. Sedimentol., Spec. Publ. 6 345–354.
Gustavson T C 1978 Bedforms and stratification types of modern gravel meander lobes, Nueces river, Texas; Sedimentology 25 401–426.
Haszeldine R S 1983 Fluvial bars reconstructed from a deep, straight channel, Upper carboniferous coalfield of northeast England; J. Sedim. Petrol. 53 1233–1248.
Hein F J and Walker R G 1977 Bar evolution and development of stratification in the gravelly, braided Kicking Horse River, British Columbia; Can. J. Earth Sci. 14 562–570.
Hjellbakk A 1997 Facies and fluvial architecture of a high-energy braided river: The upper proterozoic seglodden member, Varanger Peninsula, northern Norway; Sedim. Geol. 114 131–161.
Hoey T 1992 Temporal variations in bedload transport rates and sediment storage in gravel-bed Rivers; Progr. Phys. Geogr. 16 319–338.
Holbrook J, Scott R W and Oboh-Ikuenobe F E 2006 Base-level buffers and buttresses: A model for upstream versus downstream control on fluvial geometry and architecture within sequences; J. Sedim. Res. 76(1) 162–174.
Hornung J and Aigner T 1999 Reservoir and aquifer characterization of fluvial architectural elements: Stubensandstein, upper Triassic, southwest Germany; Sedim. Geol. 129 215–280.
Jackson R G 1976 Depositional model of point bars in the lower Wabash River; J. Sedim. Petrol. 46 579–594.
Janssens M M, Kasse C, Bohncke S J P, Greaves H, Cohen K M, Wallinga J and Hoek W Z 2012 Climate-driven fluvial development and valley abandonment at the last glacial–interglacial transition (Oude IJssel–Rhine, Germany); Netherlands J. Geosci./Geol. Mijnbouw 91 37–62.
Jo H R and Chough S K 2001 Architectural analysis of fluvial sequences in the northwestern part of Kyongsang Basin (Early Cretaceous), SE Korea; Sedim. Geol. 144 307–334.
Jones C M and McCabe P J 1980 Erosion surfaces within giant fluvial cross-beds of the Carboniferous in northern England; J. Sedim. Petrol. 50 613–620.
Kasse C, Van Balen R T, Bohncke S J P and Wallinga Vreugdenhil J M 2016 Climate and base-level controlled fluvial system change and incision during the last glacial–interglacial transition, Roer river, the Netherlands – western Germany; Netherlands J. Geosci./Geol. Mijnbouw, https://doi.org/10.1017/njg.2016.50.
Khanolkar S, Saraswati P and Rogers K 2017 Ecology of foraminifera during the middle Eocene climatic optimum in Kutch, India; Geodinamica Acta 29(2) 181–193.
Kirk M 1983 Bar developments in a fluvial sandstone (Westphalian “A”), Scotland; Sedimentology 30 727–742.
Kraus M J 1999 Paleosols in clastic sedimentary rocks: Their geological applications; Earth-Sci. Rev. 47 41–70.
Kumar P, Saraswati P K and Banerjee S 2009 Early miocene shell concentration in the mixed carbonate–siliciclastic system of Kutch and their distribution in sequence stratigraphic framework; J. Geol. Soc. India 74 432–444.
Lander R H, Bloch S, Mehta S and Atkinson C D 1991 Burial diagenesis of paleosols in the giant Yacheng gas field, People’s Republic of China: Bearing on illite reactivation pathways; J. Sedim. Petrol. 61 256–268.
Lawrence K T, Liu Z and Herbert T D 2006 Evolution of the eastern tropical Pacific through Plio-Pleistocene glaciation; Science 312(5770) 79–83.
Less G, Frijia G, Özcan E, Saraswati P K, Parente M and Kumar P 2018 Nummulitids, lepidocyclinids and Sr-isotope data from the Oligocene of Kutch (western India) with chronostratigraphic and paleobiogeographic evaluations; Geodinamica Acta 30(1) 183–211.
Levey R A 1978 Bedform distribution and internal stratification of coarse-grained point bars, upper Congaree river, South Carolina; In: Fluvial sedimentology (ed.) Miall A D, Canadian Soc. Petrol. Geol. Memoir, pp. 105–127.
Lisiecki L E and Raymo M E 2005 A Pliocene–Pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18O records; Paleoceanography 20 PA1003.
Long D G F 2011 Architecture and depositional style of fluvial systems before land plants: A comparison of Precambrian, early Paleozoic and modern river deposits from river to rock record: The preservation of fluvial sediments and their subsequent interpretation; SEPM (Soc. Sedim. Geol.) 97 37–61.
Lunt D, Foster G, Haywood A and Stone E 2008 Late Pliocene Greenland glaciation controlled by a decline in atmospheric CO2 levels; Nature 454(7208) 1102–1105.
Martinez-Garcia A, Rosell-Mele A, McClymont E L, Gersonde R and Haug G H 2010 Subpolar link to the emergence of the modern equatorial Pacific cold tongue; Science 328(5985) 1550–1553.
McKay R, Naish T, Carter L, Riesselman C, Dunbar R, Sjunneskog C, Winter D, Sangiorgi F, Warren C, Pagani M, Schouten S, Willmott V, Levy R, DeConto R and Powell R D 2012 Antarctic and Southern Ocean influences on late Pliocene global cooling; Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 109(17) 6423–6428.
McKee E and Weir G W 1953 Terminology for stratification and cross-stratification in sedimentary rocks; Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 64 381–390.
Miall A D 1977 A review of the braided river depositional environment; Earth-Sci. Rev. 13 1–62.
Miall A D 1985 Architectural-element analysis: A new method of facies analysis applied to fluvial deposits; Earth-Sci. Rev. 22 261–308.
Miall A D 1986 Eustatic sea level changes interpreted from seismic stratigraphy: A critique of methodology with particular references to the North Sea Jurassic record; AAPG Bull. 70(2) 131–137.
Miall A D 1988 Architectural elements and bounding surfaces in fluvial deposits: Anatomy of the Kayenta Formation (Lower Jurassic), southwest Colorado; Sedim. Geol. 55(3–4) 233–262.
Miall A D 1992 Alluvial deposits; In: Facies Models – Response to Sea Level Change (eds) Walker R G and James N P, Geological Association of Canada, pp. 119–142.
Miall A D 1996 The geology of fluvial deposits-sedimentary facies, basin analysis, and petroleum geology; 1st edn, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 582p.
Miall A D 2006 Reconstructing the architecture and sequence stratigraphy of the preserved fluvial record as a tool for reservoir development: A reality check; Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 90 989–1002.
Miall A D 2013 The geology of fluvial deposits: Sedimentary facies, basin analysis, and petroleum geology; 4th edn, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 582p.
Miall A D and Jones B G 2003 Fluvial architecture of the Hawkesbury Sandstone (Triassic), near Sydney, Australia; J. Sedim. Res. 73 531–545.
Miller G, Kominz M A, Browning J V, Wright J D, Mountain G S, Katz M E, Sugarman P J, Cramer B S, Christie-Blick N and Pekar S F 2005 The Phanerozoic record of global sea-level change; Science 310 1293–1298.
Miller K G, Wright J D, Browning J V, Kulpecz A, Kominz M, Naish T R, Cramer B S, Rosenthal Y, Peltier W R and Sosdian S 2012 High tide of the warm Pliocene: Implications of global sea level for Antarctic deglaciation; Geology 40 407–410.
Naafs B D A, Stein R, Hefter J, Khélifi N, De Schepper S and Haug G H 2010 Late Pliocene changes in the North Atlantic Current; Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 298 434–442.
Nanson G C 1986 Episodes of vertical accretion and catastrophic stripping: A mode of disequilibrium floodplain development; Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 97 1467–1475.
Pandey J 1982 Chronostratigraphic correlation of the Neogene sedimentaries of western Indian shelf, Himalaya and Upper Assam; Plaeontol. Soc. India, Spec. Publ. 1 95–129.
Plint A G and Nummedal D 2000 The falling stage systems tract: Recognition and importance in sequence stratigraphic analysis; In: Sedimentary responses to forced regression (eds) Hunt D and Gawthorpe R L; Geol. Soc. London, Spec. Publ. 172 1–18.
Posamentier H W and Allen G P 1993 Variability of the sequence stratigraphic model: Effects of local basin factors; Sedim. Geol. 86 91–109.
Raju D S N 1974 Study of Indian Miogypsinoidae, Kutch; In: Utrecht micropaleontological Bulletins (eds) Drooger C W and Krips Repro Meppel, Netherlands 9 13–53.
Raju D S N 1991 Miogypsina scale and Indian chronostratigraphy; Geosci. J. 12 53–65.
Raju D S N 2011 Oligo-Miocene larger foraminiferal zones of India and their importance in classification and correlation; ONGC Bull. 46 40–62.
Ramos A and Sopena A 1983 Gravel bars in low sinuosity streams (Permian and Triassic, Central Spain); In: Modern and Ancient Fluvial Systems (eds) Collinson J D and Lewis J, Int. Assoc. Sedimentol., Spec. Publ. 6 301–312.
Ravelo A C, Andreasen D H, Lyle M, Olivarez Lyle A and Wara M W 2004 Regional climate shifts caused by gradual global cooling in the Pliocene Epoch; Nature 429 263–267.
Retallack R J 1988 Field recognition of paleosols; In: Paleosols and Weathering through Geologic Time: Principles and Applications (eds) Reinhardt J and Sigleo W R, Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Paper 216 1–21.
Reuter M, Piller W E, Harzhauser M and Kroh A 2013 Cyclone trends constrain monsoon variability during late Oligocene Sea level highstands (Kachchh Basin, NW India); Clim. Past 9 2101–2115.
Rust B R 1972 Structure and process in braided river; Sedimentology 18 221–245.
Samanta B K and Lahiri A 1985 The occurrence of Discocyclina Gümbel in the middle Eocene Fulra limestone of Cutch, Gujarat, Western India, with notes on species reported from the Indian region; Bull. Geol. Min. Metallur. Soc. India 52 211–295.
Saraswati P K 1994 Biometric study of Lepidocyclina (Nephrolepidina) from Kutch, Saurashtra, and Quilon (India); J. Geol. Soc. India 44 79–90.
Saraswati P K 1995 Biometry of early Oligocene Lepidocyclina from Kutch, India; Mar. Micropaleontol. 26 303–311.
Saraswati P K, Sarkar U and Banerjee S 2012 Nummulites solitaries – Nummulites burdigalensis lineage in Kutch with remarks on the age of Naredi formation; J. Geol. Soc. India 79 476–482.
Saraswati P K, Khanolkar S, Raju D S N, Dutta S and Banerjee S 2014 Foraminiferal biostratigraphy of lignite mines of Kutch, India: Age of lignite and fossil vertebrates; J. Palaeogeogr. 3(1) 90–98.
Saraswati P K, Banerjee S, Sarkar U, Chakraborty S and Khanolkar S 2016 Eocene depositional sequence and cycles in Kutch; Geol. Soc. India Spec. Publ. 6 46–56.
Saraswati P K, Khanolkar S and Banerjee S 2018 Paleogene stratigraphy of Kutch, India: An update about progress in foraminiferal biostratigraphy; Geodinamica Acta 30 100–118.
Sarkar S, Samanta P, Mukhopadhyay S and Bose P K 2012a Stratigraphic architecture of the Sonia Fluvial interval, India in its Precambrian context; Precamb. Res. 2012 210–226.
Sarkar U, Banerjee S and Saraswati P K 2012b Integrated borehole and outcrop study for documentation of sea level cycles within the Early Eocene Naredi Formation, western Kutch, India; J. Palaeogeogr. 1 126–137.
Schumm S A 1993 River response to base level change: Implications for sequence stratigraphy; J. Geol. 101 279–294.
Schumm S A and Lichty R W 1963 Channel widening and floodplain construction along Cimarron River, southwestern Kansas: U.S.; Geol. Surv. Prof. Paper 352-E.
Schwertmann U 1993 Relations between iron oxides, soil color, and soil formation; Soil Color (soilcolor) 31 51–69.
Sengupta S, Syed R and Sarkar S 2015 Preliminary report on the wall overgrowth in some lower Oligocene reticulate Nummulites (Foraminiferida), SW Kutch, India; J. Palaeontol. Soc. India 60 85–87.
Shanley K W and McCabe P J 1993 Alluvial stratigraphy in a sequence stratigraphic framework: A case history from the Upper Cretaceous of Southern Utah, USA; In: The Geological Modelling of Hydrocarbon Reservoirs and Outcrop Analogues (eds) Flint S S and Bryant I D; Int. Assoc. Sedimentol., Spec. Publ. 15 21–56.
Shekhar S, Shukla A and Kumar P 2018 Sedimentary record of forced regression along the margin of Kutch basin: Terminal Cenozoic succession (Sandhan Formation), western India; J. Indian Assoc. Sedimentol. 35(1) 23–35.
Smith N D 1970 The braided stream depositional environment: Comparison of the Platte River with some Silurian clastic rocks, North-Central Appalachians; Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 81 2993–3014.
Smith N D 1971 Transverse bars and braiding in the lower Platte River, Nebraska; Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 82(12) 3407–3420.
Smith N D 1972 Some sedimentological aspects of planar cross-stratification in a sandy braided river; J. Sedim. Petrol. 42 624–634.
Smith D G 1983 Anastomosed fluvial deposits: Modern examples from western Canada; In: Modern and ancient fluvial systems (eds) Collinson J D and Lewin J; Int. Assoc. Sedimentol., Spec. Publ. 6 155–168.
Smith S A 1990 The sedimentology and accretionary styles of an ancient gravel-bed stream: The Budleigh Salterton Pebble Beds (Lower Triassic), southwest England; Sedim. Geol. 67 199–219.
Tandon S K and Gibling M R 1997 Calcretes at sequence boundaries in upper Carboniferous cyclothems of the Sydney Basin, Atlantic Canada; Sedim. Geol. 112 43–67.
Tebbens L A, Veldkamp A, Westerhoff W and Kroonenberg S B 1999 Fluvial incision and channel downcutting as a response to Late glacial and Early Holocene climate change: The lower reach of the River Meuse, The Netherlands; Quat. J. Sci. 14 59–75.
Van Wagoner J C 1995 Overview of sequence stratigraphy of foreland basin deposits: Terminology, summary of papers, and glossary of sequence stratigraphy; In: Sequence Stratigraphy of Foreland Basin Deposits (eds) Van Wagoner J C and Bertram G T, Am. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. Memoir 64.
Van Couvering J, Castradori D, Cita M B, Hilgen F J and Rio D 2004 The base of the Zanclean stage and of the Pliocene Series; Episodes 23 179–187.
Vandenberghe J 1993 Changing fluvial processes under changing periglacial conditions; Zeitschrift Fur Geomorphologie Supplement Band 88 17–28.
Vandenberghe J, Kasse C, Bohncke S and Kozarski S 1994 Climate-related river activity at the Weichselian-Holocene transition: A comparative study of the Warta and Maas Rivers; Terra Nova 6(5) 476–485.
Webb G E 1994 Paleokarst, paleosol, and rocky-shore deposits at the Mississippian–Pennsylvanian unconformity, northwestern Arkansas; Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 106 634–648.
Wright V P 1994 Paleosols in shallow marine carbonate sequences; Earth-Sci. Rev. 35 367–395.
Wright V P and Marriott S B 1993 The sequence stratigraphy of fluvial depositional systems: The role of floodplain sediment storage; Sedim. Geol. 86 203–210.
Wynne A B 1872 Memoir on the geology of Kutch, to accompany the map compiled by Wynne A B and Fedden F during the session 1867–68, 1868–69; Geol. Surv. India Memoirs 19(2) 269.
Acknowledgements
PK acknowledges the scientific project and financial support from the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Grant letter DST No: SR/FTP/ES-102/2014 to carry out this research work. The infrastructure facility extended by the Department of Geology, University of Delhi, is thankfully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PK: Problem visualization, field work, data acquisition and manuscript writing. SS and AS: Data acquisition, field work, map and figure construction. PPC: Scientific input and manuscript writing.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Santanu Banerjee
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, P., Shekhar, S., Shukla, A. et al. Facies architecture and spatio-temporal depositional variability in the Pliocene Sandhan fluvial system, Kutch Basin, India. J Earth Syst Sci 130, 237 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-021-01730-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-021-01730-y